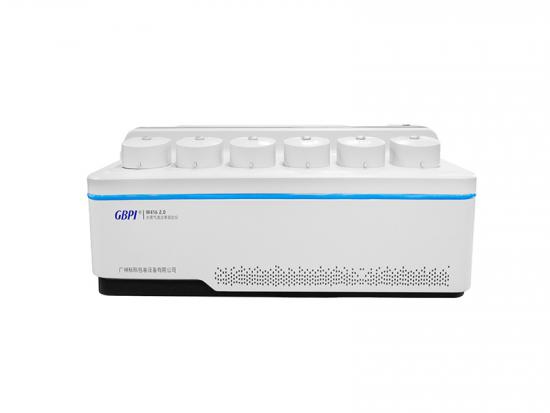
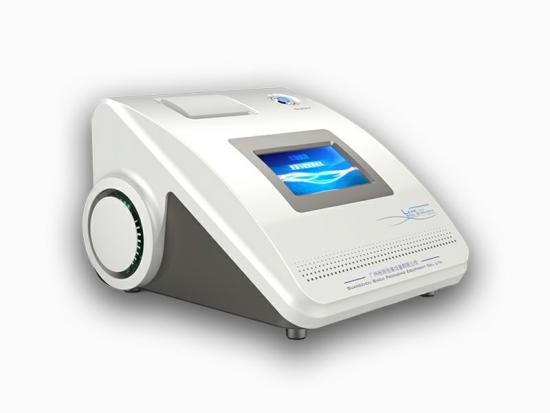
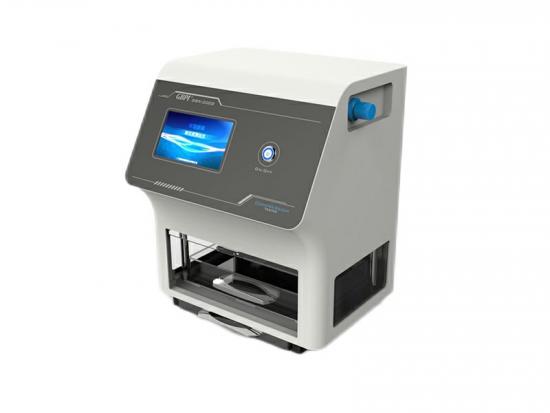
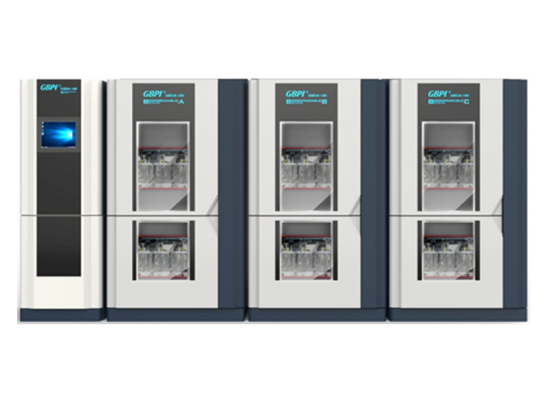
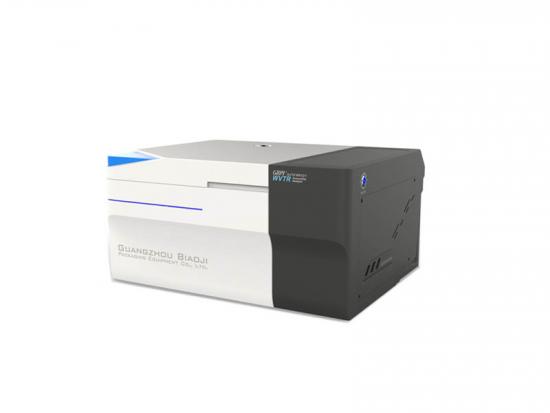
[Introduction] Separation membranes, as materials with special selective permeability, enable precise separation, purification, and concentration of substances at a molecular or microscopic particle level. They are widely used in numerous core sectors such as water treatment, food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals & petrochemicals, and energy. The stability of their performance directly determines the production efficiency and product quality in these related industries. Gas barrier property, being a core indicator for evaluating separation membrane performance, is crucial for ensuring separation purity and efficiency. The following sections provide a systematic analysis covering classification, test methods, core instruments, and actual test results. ▍1. Classification of Separation Membranes The separation capability of membranes stems from their "selective permeability." Different types of separation membranes achieve substance separation through different principles, and the gas barrier property directly affects the purity and efficiency of the separation process: Microfiltration / Ultrafiltration Membranes: Rely on membrane pore size screening for solid-liquid or macromolecule separation (e.g., intercepting suspended solids in wastewater treatment, separating proteins in biopharmaceuticals). Insufficient gas barrier properties can lead to permeation of impurity gases, affecting product purity. Reverse Osmosis / Nanofiltration Membranes: Rely on selective permeation under pressure driving force for desalination or small molecule separation (e.g., seawater desalination, drinking water softening). Poor gas barrier properties can reduce water flux and desalination rate. Pervaporation Membranes (e.g., PVA membrane): Used for separating close-boiling mixtures like alcohol-water or organic-water mixtures. The gas barrier property directly determines separation selectivity – if the target gas permeates easily, separation efficiency can be significantly compromised. Inorganic Ceramic Membranes (e.g., Alumina membrane): Suitable for separation under high-temperature and highly corrosive conditions (e.g., high-temperature fluid filtration in chemical industry). Their barrier property, along with mechanical strength, determines separation stability in harsh environments. ▍2. Test Method The performance indicators of separation membranes include separation efficiency, flux, barrier property, stability, and service life. Among these, barrier property testing is a key link in evaluating the comprehensive performance of separation membranes, directly determining their suitability and reliability in complex application scenarios. Referencing GB/T 1038.1-2022 "Plastics - Film and Sheeting - Determination of Gas Transmission Rate - Part 1: Differential-Pressure Method", the differential pressure method is adopted as the core testing method. This method quantifies the rate at which gas p...
View More

 info@gbtest.cn
info@gbtest.cn

 en
en ru
ru es
es ar
ar










